Application for the Web-IO Digital:
Bridging distances
Tunneling signals of an alarm system through the network

Definition of tasks
A company has two business locations in a town. The main business location accommodates the administration and central warehouse. For protection against burglary, motion detectors which are all connected to a central alarm system are installed on a wide scale. The production is located at the second business location and this is linked IT-technically to the main location via a WAN connection.
On the second business location too, motion detectors are to be installed which must also be connected with the central alarm system. In the event of an alarm, a warning light and a horn are to be switched on.
In order to save the costs of a dedicated line, the signals must also be carried via the existing WAN link.
The solution
A Web-IO 12+12 digital was employed at each business location. The two Web-IOs were connected by box-to-box mode in such a way that changes on the inputs of Web-IO A automatically update the outputs of Web-IO B - and that in both directions.
The motion detectors were connected to the inputs of Web-IO B and the warning light was connected to an output. The inputs and outputs of Web-IO A were connected with the alarm unit.
The details
-
1. At business location A, the digital outputs of one of the Web-IOs were connected with the alarm unit. At business location B, the motion detectors and the warning light were connected to the Web-IO.

-
2. The Web-IO was plugged into a free Ethernet port and connected to a power supply.

-
3. The Web-IO was assigned an IP address.
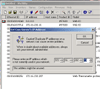
-
4. Via the browser, the two Web-IOs were configured in box-to-box mode.
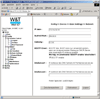
In box-to-box mode, digital signals can be tunneled through the network across the business locations - if the network infrastructure permits this, then worldwide.